Options
Recent Advances in the Therapeutic Potential of Bioactive Molecules from Plants of Andean Origin
Journal
Nutrients
ISSN
2072-6643
Date Issued
2025-05-22
Author(s)
Carlos Barba-Ostria
Jéssica Guamán-Bautista
Augusto A. Tosi-Vélez
Juan A. Puente-Pineda
Melanie A. Cedeño-Zambrano
Enrique Teran
Linda P. Guamán
Abstract
Background: Andean plants are rich in bioactive compounds shaped by extreme environmental conditions, contributing to their antioxidant, antimicrobial, and anti-inflammatory properties. This review explores their phytochemical composition, biological activities, and therapeutic potential in modern medicine and nutrition of three plants of Andean origin. Methods: A literature review of peer-reviewed studies was conducted, focusing on key species such as quinoa (Chenopodium quinoa), amaranth (Amaranthus spp.), and lupin (Lupinus spp.), selected for this review due to their Andean origin, long-standing role in traditional diets, and growing scientific interest in their unique phytochemical profiles and therapeutic potential. This analysis covers their phytochemistry, bioactivities, and the influence of environmental factors on compound potency. Results: These Andean-origin plants contain flavonoids, terpenoids, alkaloids, and phenolic compounds that support antioxidant, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and anticancer activities. High-altitude conditions enhance the biosynthesis of these bioactives, increasing their therapeutic value. Quinoa, amaranth, and lupin show strong potential for dietary and pharmaceutical applications, particularly in metabolic health and disease prevention. Additionally, preclinical studies and clinical trials have begun exploring the efficacy of these compounds in preventing and treating metabolic and chronic diseases. Conclusions: Andean plants are a valuable source of functional bioactive molecules with diverse health benefits. Future research should optimize cultivation strategies and explore novel applications in nutrition and medicine.
File(s)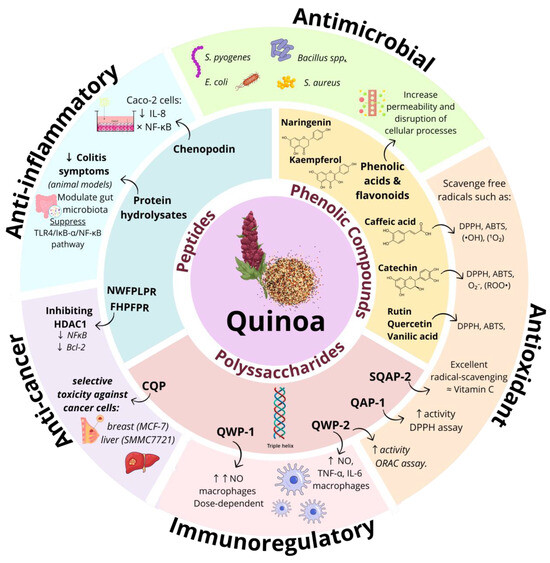
Loading...
Name
nutrients-17-01749-g002-550.jpg
Type
Personal Picture
Size
96.12 KB
Format
JPEG
Checksum
(MD5):13b657c4be6d9c32dff4e91741beb9c4