Options
Activation and Expansion of Human T-Cells Using Microfluidic Devices
Journal
Biosensors
ISSN
2079-6374
Date Issued
2025-04-25
Author(s)
Gustavo Rosero
Dario Ruarte
Julia Pinter
Vizuete, Karla
Maximiliano Perez
Marie Follo
Lerner, Betiana
Roland Mertelsmann
Abstract
Treatment of cancer patients with autologous T-cells expressing a chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) is one of the most promising therapeutic modalities for hematological malignancy treatment. For this treatment, primary T-cell expansion is needed. Microfluidic technologies can be used to better understand T-cell activation and proliferation. Microfluidics have had a meaningful impact in the way experimental biology and biomedical research are approached in general. Furthermore, microfluidic technology allows the generation of large amounts of data and enables the use of image processing for analysis. However, one of the major technical hurdles involved in growing suspension cells under microfluidic conditions is their immobilization, to avoid washing them out of the microfluidic chip during medium renewal. In this work, we use a multilevel microfluidic chip to successfully capture and immobilize suspension cells. Jurkat cells and T-cells are isolated through traps to microscopically track their development and proliferation after activation over a period of 8 days. The T-cell area of four independent microchannels was compared and there is no statistically significant difference between them (ANOVA p-value = 0.976). These multilevel microfluidic chips provide a new method of studying T-cell activation.
File(s)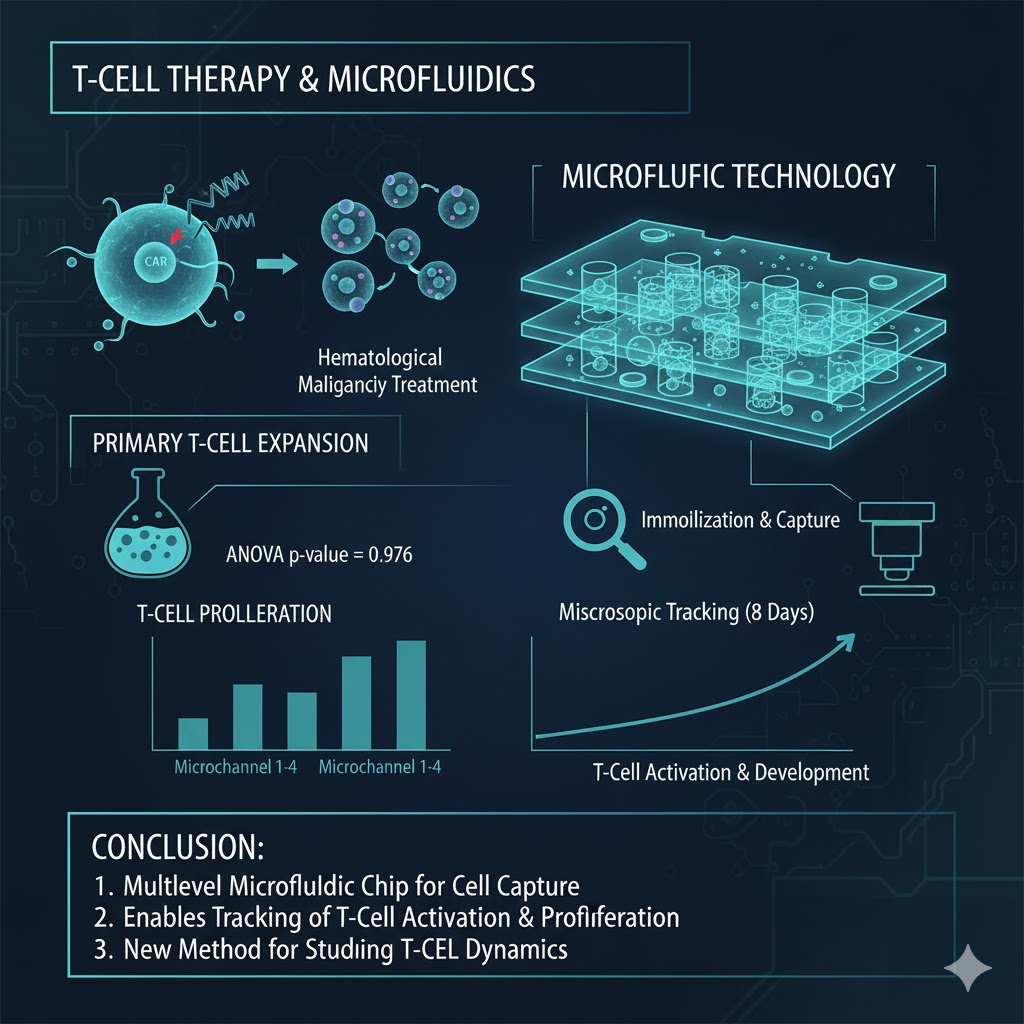
Loading...
Name
1.jpg
Type
Personal Picture
Size
178.81 KB
Format
JPEG
Checksum
(MD5):11a68438b3c186a5d701ec2aa7822b32